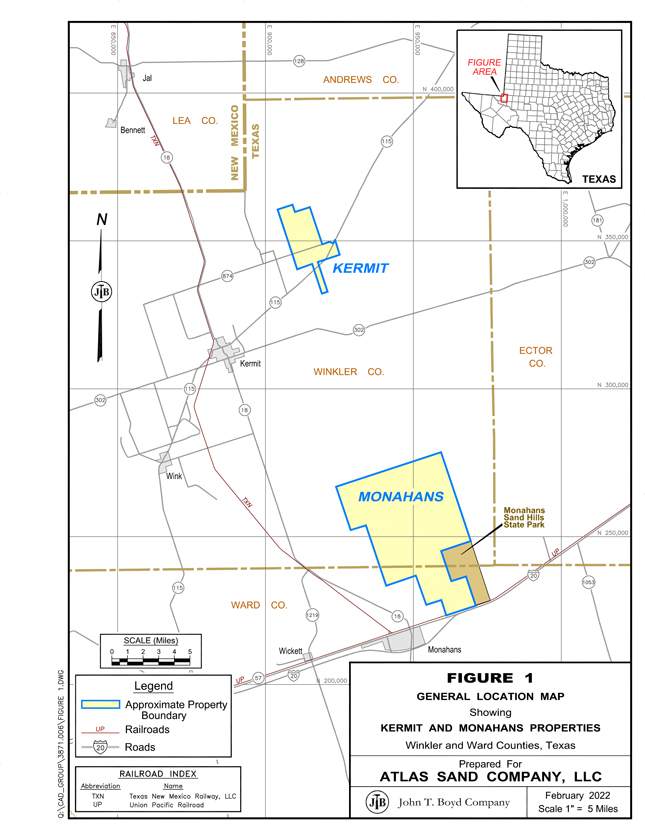
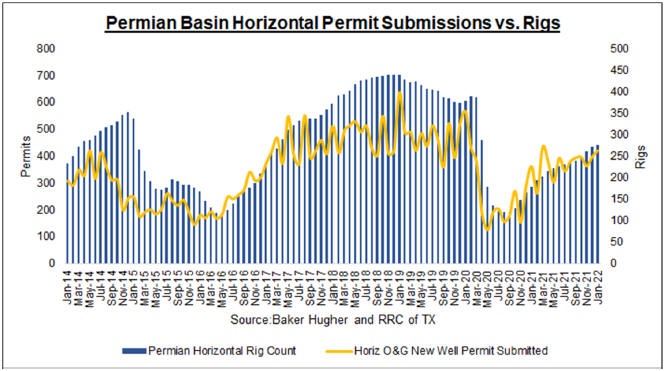
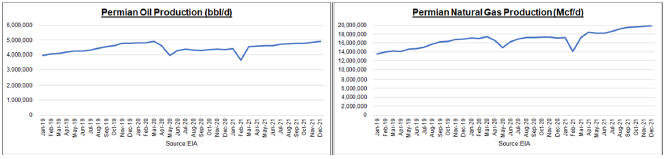
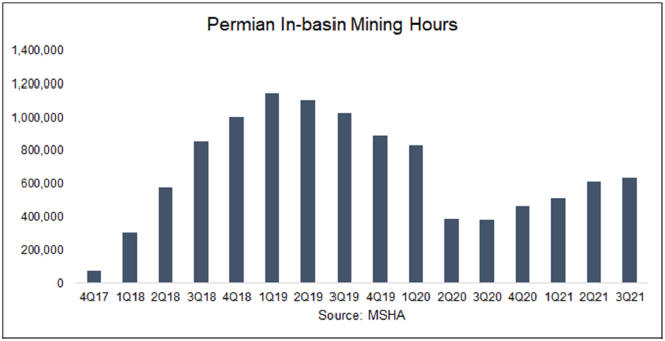
requirements. Our objective is to utilize the original report as a basis and incorporate additional
information that we have reviewed into compiling an updated compliant technical report summary contained herein. The estimates within this report are adjusted to reflect an “as of” date of December 31, 2021.
The results of our review, presented in report form herein, were prepared in accordance with the disclosure requirements set forth in Subpart 1300 and Item
601(b)(96) of the SEC’s Regulation S-K. The purpose of this report is threefold: (1) to summarize available information for the subject mining properties, (2) to provide the conclusions of our
technical audit, and (3) to provide a statement of frac sand resources and reserves for the Kermit and Monahans mines. This is the first technical report summary filed by Atlas for the mines.
BOYD’s findings are based on our detailed examination of the supporting geologic, technical, and economic information provided by Atlas in formulating
the estimates of frac sand resources and reserves disclosed in this report. We independently estimated the frac sand resources and reserves from first principles based on third-party exploration information provided to BOYD.
We used standard engineering and geoscience methods, or a combination of methods, that we considered to be appropriate and necessary to establish the
conclusions set forth herein. As in all aspects of mining property evaluation, there are uncertainties inherent in the interpretation of engineering and geoscience data; therefore, our conclusions necessarily represent only informed professional
judgment.
The ability of Atlas, or any mine operator, to recover all of the estimated frac sand reserves presented in this report is dependent on
numerous factors that are beyond the control of, and cannot be anticipated by, BOYD. These factors include mining and geologic conditions, the capabilities of management and employees, the securing of required approvals and permits in a timely
manner, future sand prices, etc. Unforeseen changes in regulations could also impact performance. Opinions presented in this report apply to the site conditions and features as they existed at the time of BOYD’s investigations and those
reasonably foreseeable.
This report is intended for use by Atlas subject to the terms and conditions of its engagement agreement with BOYD. The agreement
permits Atlas to file this report as a technical report summary with the SEC pursuant to Subpart 1300 and Item 601(b)(96) of Regulation S-K. Except for the purposes legislated under US securities law, any
other uses of or reliance on this report by any third party is at that party’s sole risk. The
JOHN T. BOYD COMPANY
18